FTC Safeguards Rule:
How is the automotive industry affected?
The FTC Safeguards Rule was created to ensure that financial institutions subject to the rule take steps to protect customer information.
This includes protecting against identity theft, data breaches, and other security risks. Initially created and in effect in 2003, the updated rule applies to non-bank financial institutions such as lenders, mortgage brokers, and auto dealers. [FTC Safeguards Rule].
What are the goals of the rule?
-
- Confidentiality and Security: The rule requires financial institutions to implement safeguards to ensure the confidentiality and security of customer information. [FTC Safeguards Rule: What Your Business Needs to Know].
- Protection from Threats: Covered businesses must also have measures in place to protect customer information from anticipated threats and unauthorized access that could result in harm.
Overall, the FTC Safeguards Rule is a consumer protection measure aimed at strengthening the security of financial information held by certain financial institutions.

Rule timeline:
-
- Rule Updates and Amendments: While the core rule has existed since 2003, it underwent revisions in 2021 to address advancements in technology and strengthen security practices, and an amendment was approved in 2023 adding reporting requirements.
- Finalization Date: The FTC finalized the revisions to the Safeguards Rule in October 2021. This established the new requirements and strengthened data security measures for covered institutions [FTC Amends Safeguards Rule to Require Non-Banking Financial Institutions to Report Data Security Breaches].
- 2023 Amendment Effective Date: The amendment becomes effective May 13, 2024. This is the date when non-banking financial institutions under FTC jurisdiction must comply with the new reporting requirements for data security breaches impacting 500 or more people [Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information].
What industries are affected by the 2021 revision?
The FTC Safeguards Rule and its 2021 revision primarily targets the financial services industry, but with a specific focus on institutions outside the traditional banking sector.
Affected Industries:

Non-Bank Financial Institutions: This is the main target, encompassing businesses that deal with customer financial data but are not regulated by other financial oversight bodies.
Examples include:
-
-
- Motor Vehicle Dealerships: Financing and leasing car purchases involve handling sensitive customer financial information.
- Mortgage Lenders and Brokers: The mortgage process involves collecting and storing a significant amount of financial data.
-
-
- Payday Lenders: The short-term loan industry also deals with customer financial information.
- Investment Advisors (not SEC-registered): Financial advisors who do not register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) fall under the FTC’s purview.
- Tax Preparation Firms: Tax preparation often involves access to sensitive financial documents and data.
- Credit Counseling and Debt Collection Agencies: These entities collect and manage financial information from clients.
- Check Cashing and Wire Transfer Services: These businesses handle financial transactions and might collect customer data.
- Finders (as of the 2021 revision): Businesses that connect customers with financial products or services are also included.
- Traditional Banks (Partially): While major banks are subject to other regulations, the FTC Safeguards Rule might apply to their specific subsidiaries or affiliates that deal with customer financial data and fall outside the scope of other oversight bodies.
It’s important to note:
- The FTC website provides a more comprehensive list of examples to help businesses determine if they fall under the rule: https://www.ftc.gov/
- Businesses should consult with legal counsel to ensure compliance with the FTC Safeguards Rule and its amendments.
How is the Automotive Industry Affected?

The FTC Safeguards Rule applies specifically to dealerships that handle customer financial information due to providing loans or assistance in obtaining loans.
- Protects Customer Data: The rule mandates dealerships to create a comprehensive cybersecurity program to safeguard customer data. This data includes Social Security numbers, bank account details, and any information used for financing or leasing a car.
- Prevents Security Risks: By requiring strong security measures, the FTC aims to minimize data breaches, identity theft, and other cyber threats targeting dealerships.
Key Requirements for Dealerships:
Develop a Written Information Security Program (WISP): This document serves as the foundation of your security plan. It should detail the policies, procedures, and controls in place to safeguard sensitive customer data [FTC Safeguards Rule for Auto Dealers: What You Need to Know].
Designate a Security Officer: Appoint a qualified individual to oversee the dealership’s information security program. This person is responsible for implementing and maintaining the safeguards outlined in the WISP.
Perform a Risk Assessment: Regularly assess the potential threats and vulnerabilities facing your dealership’s data systems. This helps identify areas where security controls are needed.
Implement Access Controls: Restrict access to customer information only to authorized personnel who need it for their job duties. This might involve using passwords, multi-factor authentication, and access control lists.
Encrypt Sensitive Information: Encrypt customer data, both at rest (stored) and in transit (being transmitted) to minimize the risk of unauthorized access in case of a breach.
Implement Data Disposal Procedures: Establish secure methods for disposing of customer information when it’s no longer needed. This includes both paper records and electronic data.
Employee Training: Train your staff on cybersecurity best practices to raise awareness of potential threats and how to handle customer information securely.
While these are some of the key requirements of the FTC Safeguards Rule for automotive dealerships, it is advisable to consult with a qualified information security professional to ensure your dealership is compliant with the rule.
-
- Compliance Deadline: The deadline for dealerships to comply with the FTC Safeguards Rule was June 9, 2023. Failing to comply could result in significant fines from the FTC.
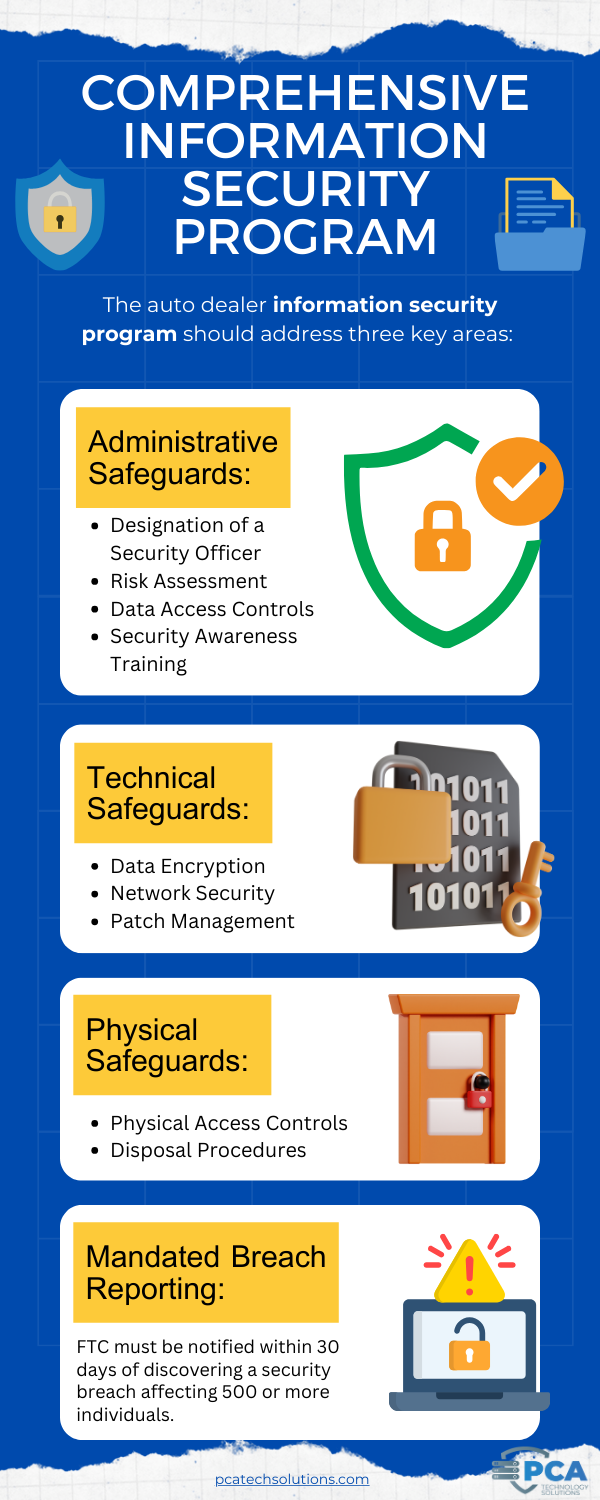
What is included in the Comprehensive Information Security Program?
Auto dealerships that handle loans are required to implement a comprehensive, written information security program (WISP) to protect customer financial data.
This program should address three key areas:
1. Administrative Safeguards:
-
- Designation of a Security Officer: Appoint someone responsible for the overall security program and data protection.
- Risk Assessment: Identify and assess potential threats and vulnerabilities to customer data.
- Data Access Controls: Establish procedures to determine who has access to customer data and what level of access they have.
- Security Awareness Training: Train employees on data security best practices and how to identify and avoid phishing attempts.
2. Technical Safeguards:
-
- Data Encryption: Encrypt customer data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access in case of a breach.
- Network Security: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other measures to protect dealership networks from cyberattacks.
- Patch Management: Regularly update software and systems with security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
3. Physical Safeguards:
-
- Physical Access Controls: Secure customer data physically, for example by restricting access to server rooms and requiring strong passwords.
- Disposal Procedures: Implement procedures for the proper disposal of customer data after it is no longer needed.
What is required if there is a data breach?
The key aspect of the FTC Safeguards Rule 2023 amendment focuses on data breach reporting. It applies to financial institutions, which includes some businesses in the automotive industry like dealerships who provide loans.
Key Change:
-
-
- Mandated Breach Reporting: The amendment requires covered financial institutions to report security incidents to the FTC. This applies to situations where unencrypted customer information of at least 500 individuals is acquired without authorization.
- The FTC requires notification within 30 days of discovering the security breach.
- Mandated Breach Reporting: The amendment requires covered financial institutions to report security incidents to the FTC. This applies to situations where unencrypted customer information of at least 500 individuals is acquired without authorization.
-
Are there penalties for not complying with the FTC Safeguard Rule?
Failing to comply with the FTC Safeguards Rule can result in several severe consequences for businesses:
-
- Financial Penalties: The FTC can impose hefty fines. The maximum penalty is $11,000 per day, per violation for a data security breach.
- There is also the possibility of FTC seeking damages for violations of previous agreements, reaching $43,000 per day, per violation.
- Litigation: Non-compliance opens businesses up to lawsuits from customers, employees, or anyone else affected by a data breach due to weak safeguards.
- Reputational Damage: News of a security breach and non-compliance can severely damage a business’s reputation, potentially leading to lost customers and business opportunities.
- Long-term Regulatory Scrutiny: The FTC can subject non-compliant businesses to extensive audits for a long time, creating a burden and further costs.
- Imprisonment (worst-case scenario): For extreme cases of negligence resulting in a breach, key personnel like directors or owners could face criminal charges and even imprisonment.
It is important to note that while the FTC might not impose the maximum penalty for first-time offenders, the potential consequences are significant. It’s always best to take steps to ensure compliance with the Safeguards Rule.
What compliance resources are available for automotive dealerships?
Information technology (IT) providers, also known as Managed Service Security Providers (MSSPs) can be valuable partners for automotive dealerships in achieving compliance with the FTC Safeguards Rule. By outsourcing to trained professionals, dealerships can ensure security is maintained.
Risk Assessment and Security Controls:
-
- Risk Assessment Expertise: IT providers can assist dealerships in conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in their data systems and infrastructure. This helps dealerships understand the specific areas where security controls are most needed.
- Security Control Implementation: IT providers can recommend and implement appropriate security controls based on the identified risks. This might involve firewalls, intrusion detection systems, data encryption solutions, and access control mechanisms.
- Security Awareness Training: Many IT providers offer security awareness training programs for dealership staff. These programs educate employees on cybersecurity best practices, phishing scams, and how to handle customer information securely.
Technical Expertise and Resources:
-
- Data Encryption: IT providers can assist dealerships with implementing data encryption solutions to protect sensitive customer information both at rest (stored) and in transit (being transmitted).
- System Monitoring and Patch Management: IT providers can offer ongoing system monitoring services to detect suspicious activity and identify potential security breaches. They can also help dealerships implement a patch management system to ensure software applications and operating systems are updated with the latest security patches.
- Data Disposal Procedures: IT providers can advise dealerships on secure methods for disposing of customer data when it is no longer needed. This includes both paper records and electronic data destruction.
Compliance Support and Guidance:
-
- Understanding the Rule: MSSPs can help dealerships understand the specific requirements of the FTC Safeguards Rule and how they apply to their operations.
- Developing a WISP: MSSPs can assist dealerships in developing and implementing a Written Information Security Program (WISP) that outlines the policies, procedures, and controls to safeguard customer data.
- Staying Updated: The IT security landscape is constantly evolving. MSSPs can help dealerships stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities and ensure their security measures remain effective.
Additional Benefits:
-
- Cost-Effectiveness: Partnering with an IT provider can be a cost-effective way for dealerships to access essential security expertise and resources, especially for smaller dealerships that might not have the in-house IT staff to manage cybersecurity effectively.
- Improved Security Posture: By leveraging the expertise of IT providers, dealerships can significantly improve their overall security posture and reduce the risk of data breaches.
The FTC provides resources and guidance to help dealerships comply with the Safeguards Rule:
Conclusion: Ensuring Compliance with FTC Safeguards Rule
By understanding the intricacies of the FTC Safeguards Rule, along with its amendments and updates, impacted industries will remain in compliance and avoid any resulting penalties.
We know this can all be quite confusing. Are you still unsure of what would be best for your company, and would like some assistance? Contact us today to ask how PCA’s expert technicians can assist with the creation of your Comprehensive Information Security Program and make the best recommendations for your business.

Ted Clouser
President & CEO, PCA Technology Solutions
Ted Clouser, PCA Technology Solutions’ President and CEO, brings a unique blend of rural Pennsylvania work ethic and a passion for technology to PCA Technology Solutions. Growing up on a dairy farm, after graduating from high school at 16, he launched his own computer business, fostering a lifelong love for the industry. In 1996, he joined PC Assistance of Little Rock, eventually acquiring the company with his wife in 2018.
A firm believer in using the power of technology to empower people, Ted broadened the company’s focus to include cybersecurity, IT consulting, managed services, and VoIP solutions. As President and CEO Ted leads by example, and holds a prestigious CISSP certification, demonstrating his commitment to staying at the forefront of the cybersecurity landscape.
Outside of work, Ted enjoys a fulfilling family life, supports several non-profit organizations, and is an active member of his church. Married to Stephanie since 1998, they have two adult children, Alexis and Ethan.